

Ambient temperature is an example of exogenous vasoconstriction. Causes įactors that trigger vasoconstriction can be exogenous or endogenous in origin. This reduction in calcium removes the stimulus necessary for contraction, allowing for a return to baseline. Once elevated, the intracellular calcium concentration is returned to its normal concentration through a variety of protein pumps and calcium exchangers located on the plasma membrane and sarcoplasmic reticulum. This enzyme is responsible for phosphorylating the light chain of myosin to stimulate cross-bridge cycling. The rise in intracellular calcium complexes with calmodulin, which in turn activates myosin light-chain kinase. Such stimuli result in a signal transduction cascade that leads to increased intracellular calcium from the sarcoplasmic reticulum through IP3-mediated calcium release, as well as enhanced calcium entry across the sarcolemma through calcium channels. These compounds interact with cell surface adrenergic receptors. Two common stimuli for eliciting smooth muscle contraction are circulating epinephrine and activation of the sympathetic nervous system (through release of norepinephrine) that directly innervates the muscle.
Hormonal or pharmacokinetic components are more physiologically relevant. Smooth muscle cells are capable of generating action potentials, but this mechanism is rarely utilized for contraction in the vasculature. However, the specific mechanisms for generating an increased intracellular concentration of calcium depends on the vasoconstrictor. The mechanism that leads to vasoconstriction results from the increased concentration of calcium (Ca 2+ ions) within vascular smooth muscle cells. Severe vasoconstriction may result in symptoms of intermittent claudication. Medications that cause vasoconstriction include: antihistamines, decongestants, and stimulants. Many vasoconstrictors also cause pupil dilation. The extent of vasoconstriction may be slight or severe depending on the substance or circumstance. Generalized vasoconstriction usually results in an increase in systemic blood pressure, but it may also occur in specific tissues, causing a localized reduction in blood flow. Medications causing vasoconstriction, also known as vasoconstrictors, are one type of medicine used to raise blood pressure.
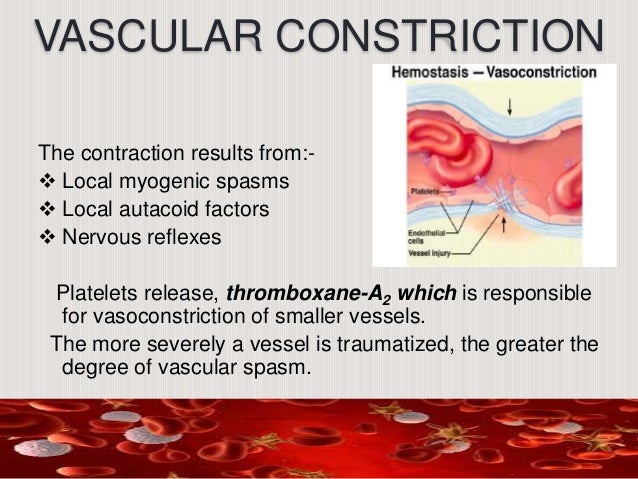
On a larger level, vasoconstriction is one mechanism by which the body regulates and maintains mean arterial pressure.
Constricting blood vessel meaning skin#
This makes the skin turn paler because less blood reaches the surface, reducing the radiation of heat. When blood vessels constrict, the flow of blood is restricted or decreased, thus retaining body heat or increasing vascular resistance. The process is particularly important in controlling hemorrhage and reducing acute blood loss. The process is the opposite of vasodilation, the widening of blood vessels. Vasoconstriction is the narrowing of the blood vessels resulting from contraction of the muscular wall of the vessels, in particular the large arteries and small arterioles.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
